|
|
D.15.9.2 hodgeIdeals
Procedure from library hodge.lib (see hodge_lib).
- Usage:
- hodgeIdeals(f, p [, eng]); f a reduced poly, p a non-negative integer, eng an optional integer.
- Return:
- ring
- Purpose:
- compute the Hodge ideals of
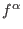 up to level up to level
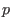 , for a reduced hypersurface , for a reduced hypersurface
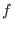 . .
- Note:
- activate the output ring with the
setring command.
In the output ring, the list of ideals hodge contains the Hodge ideals of
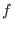 . .
The value of eng controls the algorithm used for Groebner basis computations.
See the engine procedure from dmodapp_lib for the available algorithms.
- Display:
- If
printlevel=1, progress debug messages will be printed.
Example:
| | LIB "hodge.lib";
ring R = 0,(x,y),dp;
poly f = y^2-x^3;
def Ra = hodgeIdeals(f, 2);
setring Ra; hodge;
==> [1]:
==> [1]:
==> [1]:
==> _[1]=1
==> [2]:
==> _[1]=y
==> _[2]=x
==> [3]:
==> _[1]=y^2
==> _[2]=x*y
==> _[3]=x^3
==> [2]:
==> 1/6
==> [3]:
==> 1
==> [2]:
==> [1]:
==> [1]:
==> _[1]=1
==> [2]:
==> _[1]=y
==> _[2]=x^2
==> [3]:
==> _[1]=y^3
==> _[2]=x*y^2
==> _[3]=x^2*y
==> _[4]=x^3+(2*a+1)*y^2
==> [2]:
==> 5/6
==> [3]:
==> 1
==> [3]:
==> [1]:
==> [1]:
==> _[1]=y
==> _[2]=x
==> [2]:
==> _[1]=y^2
==> _[2]=x*y
==> _[3]=x^3
==> [3]:
==> _[1]=y^3
==> _[2]=x^2*y^2
==> _[3]=x^3*y
==> _[4]=x^4+(2*a+1)*x*y^2
==> [2]:
==> 1
==> [3]:
==> 1
|
|



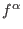 up to level
up to level
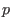 , for a reduced hypersurface
, for a reduced hypersurface
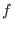 .
.
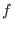 .
.